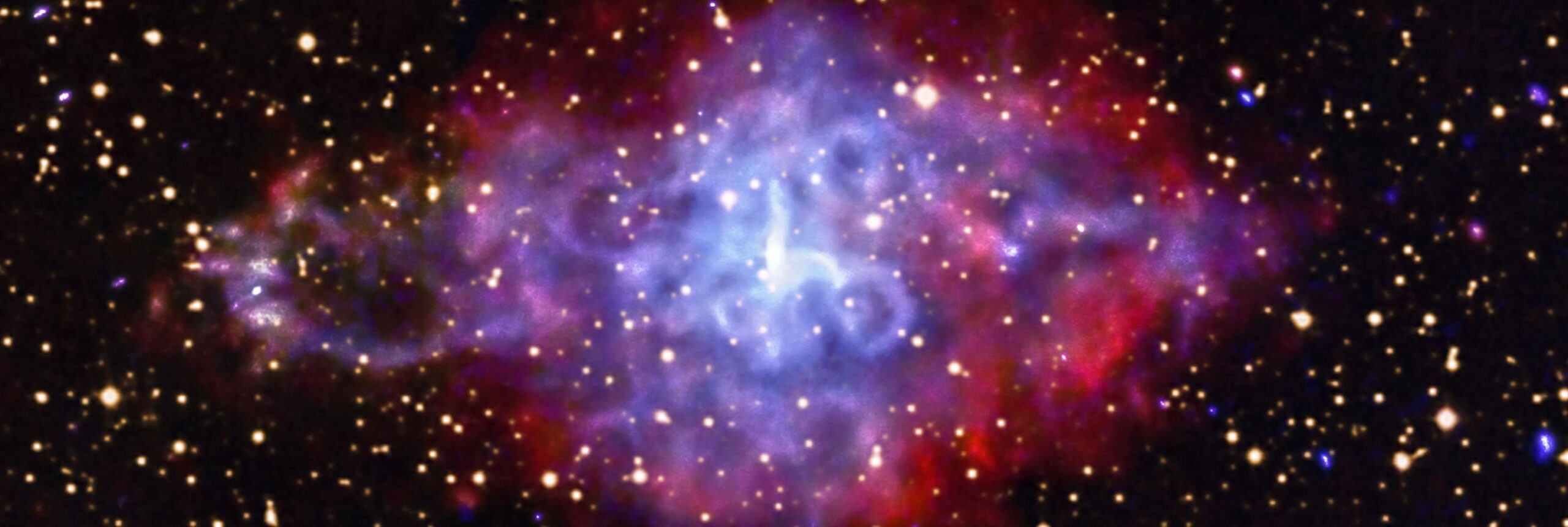
NASA’s Webb Depicts Staggering Structure in 19 Nearby Spiral Galaxies
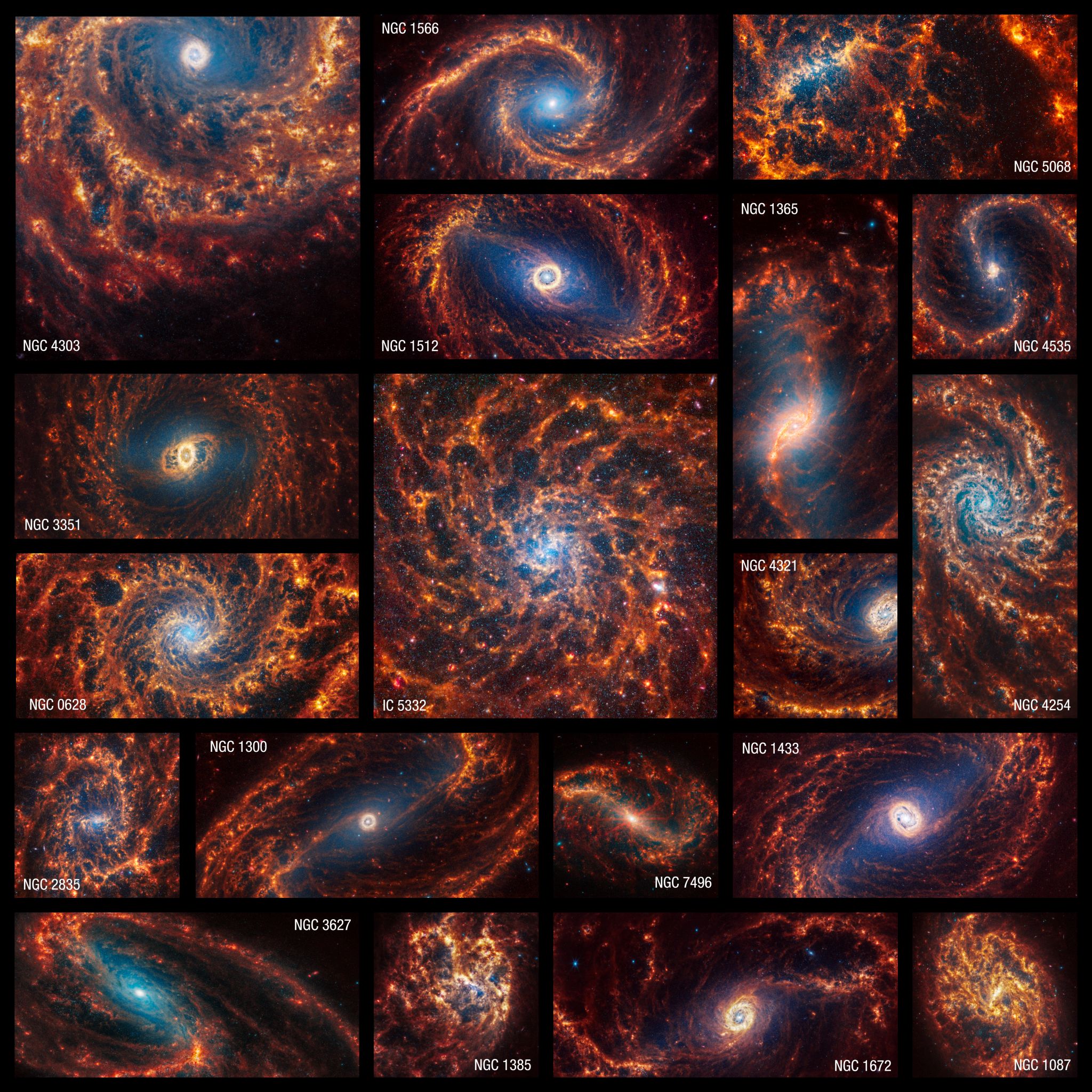

It’s oh-so-easy to be absolutely mesmerized by these spiral galaxies. Follow their clearly defined arms, which are brimming with stars, to their centers, where there may be old star clusters and – sometimes – active supermassive black holes. Only NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope can deliver highly detailed scenes of nearby galaxies in a combination of near- and mid-infrared light – and a set of these images was publicly released today.

The James Webb Space Telescope observed 19 nearby face-on spiral galaxies in near- and mid-infrared light as part of its contributions to the Physics at High Angular resolution in Nearby GalaxieS (PHANGS) program. PHANGS also includes images and data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, the Very Large Telescope’s Multi-Unit Spectroscopic Explorer, and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array, which included observations taken in ultraviolet, visible, and radio light.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Janice Lee (STScI), Thomas Williams (Oxford), PHANGS Team, Elizabeth Wheatley (STScI)
These Webb images are part of a large, long-standing project, the Physics at High Angular resolution in Nearby GalaxieS (PHANGS) program, which is supported by more than 150 astronomers worldwide. Before Webb took these images, PHANGS was already brimming with data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, the Very Large Telescope’s Multi-Unit Spectroscopic Explorer, and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array, including observations in ultraviolet, visible, and radio light. Webb’s near- and mid-infrared contributions have provided several new puzzle pieces.
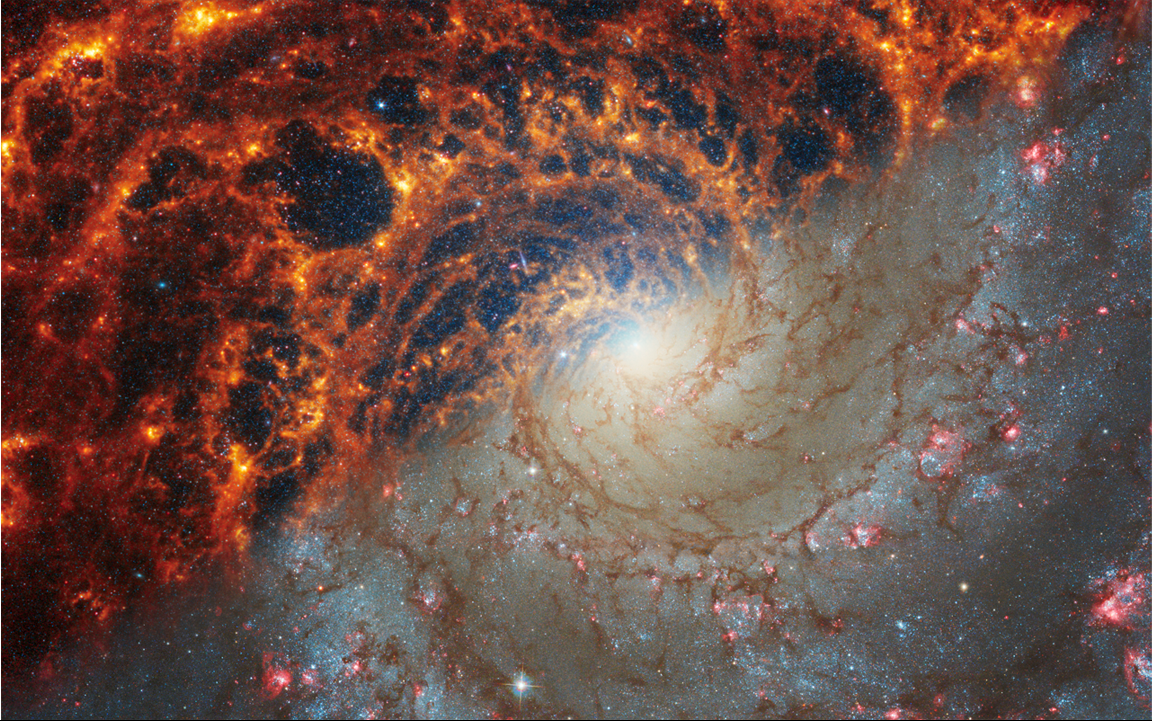

Face-on spiral galaxy, NGC 628, is split diagonally in this image: The James Webb Space Telescope’s observations appear at top left, and the Hubble Space Telescope’s on bottom right. Webb and Hubble’s images show a striking contrast, an inverse of darkness and light. Why? Webb’s observations combine near- and mid-infrared light and Hubble’s showcase visible light. Dust absorbs ultraviolet and visible light, and then re-emits it in the infrared. In Webb’s images, we see dust glowing in infrared light. In Hubble’s images, dark regions are where starlight is absorbed by dust.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Janice Lee (STScI), Thomas Williams (Oxford), and the PHANGS team

Hubble’s image of NGC 628 shows a densely populated face-on spiral galaxy anchored by its central region, which has a light yellow haze that takes up about a quarter of the view. The core is brightest at the center, washing out light from other objects. Delicate spiral arms start near the center and extend to the edges, rotating counterclockwise. There is more brown dust beginning at the center, but as the arms extend outward, brown dust lanes alternate with diffuse lines of bright blue stars. Throughout the spiral arms, there are bright pink patches of star-forming clusters.
NASA, STScI

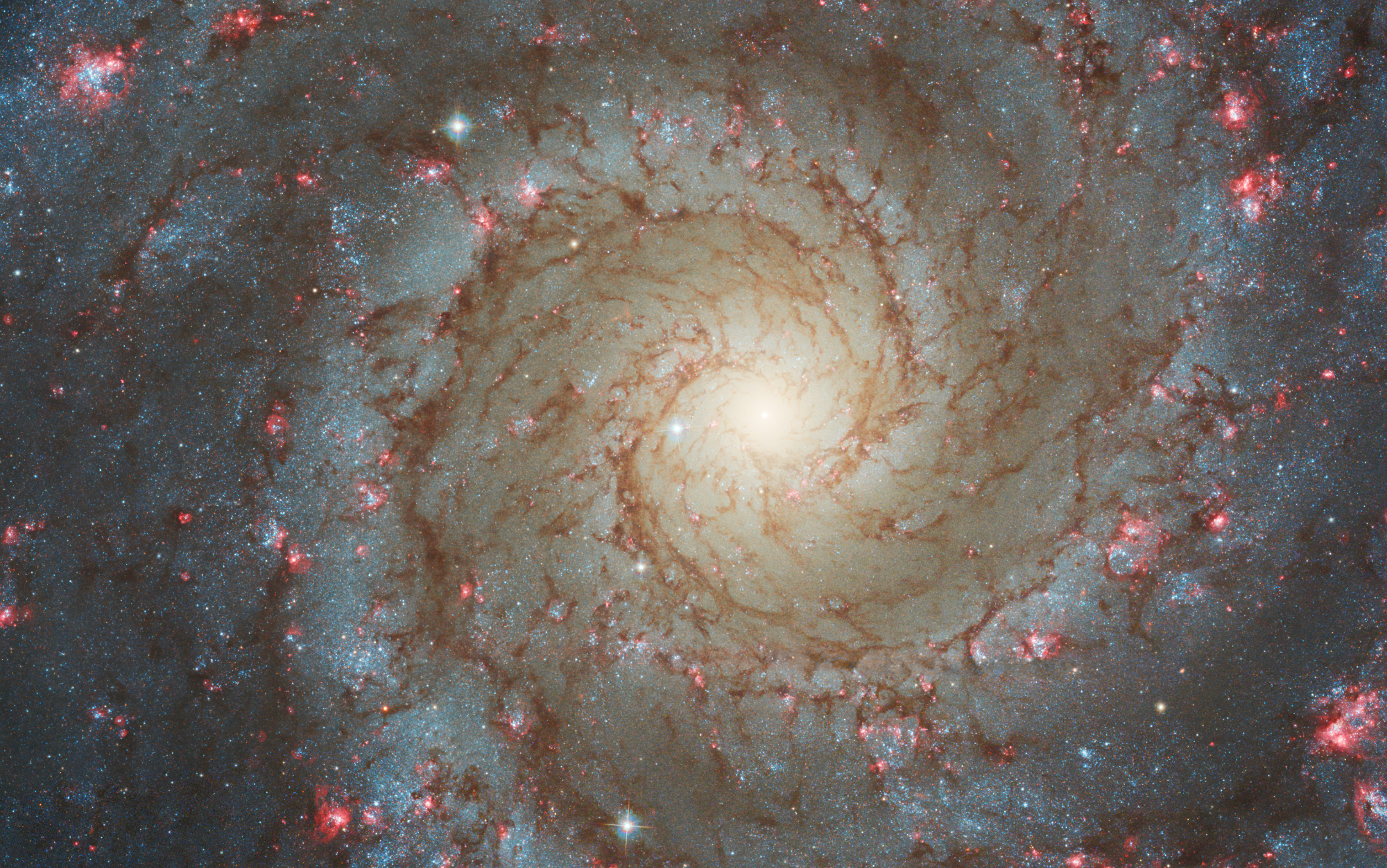
Spiral galaxy NGC 628 is 32 million light-years away in the constellation Pisces. Webb’s image of NGC 628 shows a densely populated face-on spiral galaxy anchored by its central region, which has a light blue haze that takes up about a quarter of the view. In this circular core is the brightest blue area. Within the core are populations of older stars, represented by many pinpoints of blue light. Spiny spiral arms made of stars, gas, and dust also start at the center, largely starting in the wider area of the blue haze. The spiral arms extend to the edges, rotating counterclockwise. The spiraling filamentary structure looks somewhat like a cross section of a nautilus shell. The arms of the galaxy are largely orange, ranging from dark to bright orange. Scattered across the packed scene are some additional bright blue pinpoints of light, which are stars spread throughout the galaxy. In areas where there is less orange, it is darker, and some dark regions look more circular. A prominent dark “bubble” appears to the top left of the blue core. And a wider, elliptical “bubble” to the bottom right.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Janice Lee (STScI), Thomas Williams (Oxford), and the PHANGS team
“Webb’s new images are extraordinary,” said Janice Lee, a project scientist for strategic initiatives at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. “They’re mind-blowing even for researchers who have studied these same galaxies for decades. Bubbles and filaments are resolved down to the smallest scales ever observed, and tell a story about the star formation cycle.”
Excitement rapidly spread throughout the team as the Webb images flooded in. “I feel like our team lives in a constant state of being overwhelmed – in a positive way – by the amount of detail in these images,” added Thomas Williams, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom.
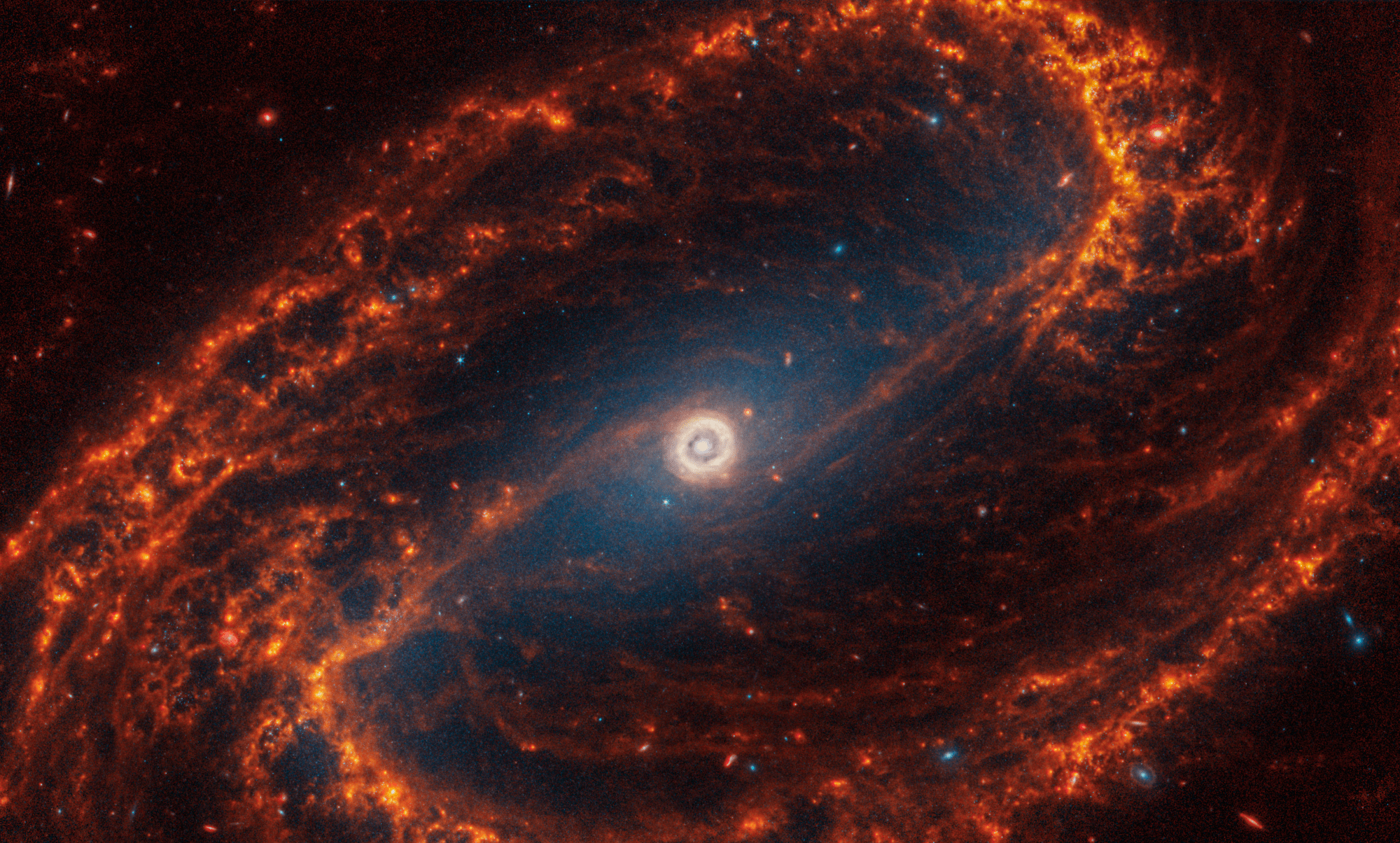
Spiral galaxy NGC 1300 is 69 million light-years away in the constellation Eridanus.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Janice Lee (STScI), Thomas Williams (Oxford), and the PHANGS team
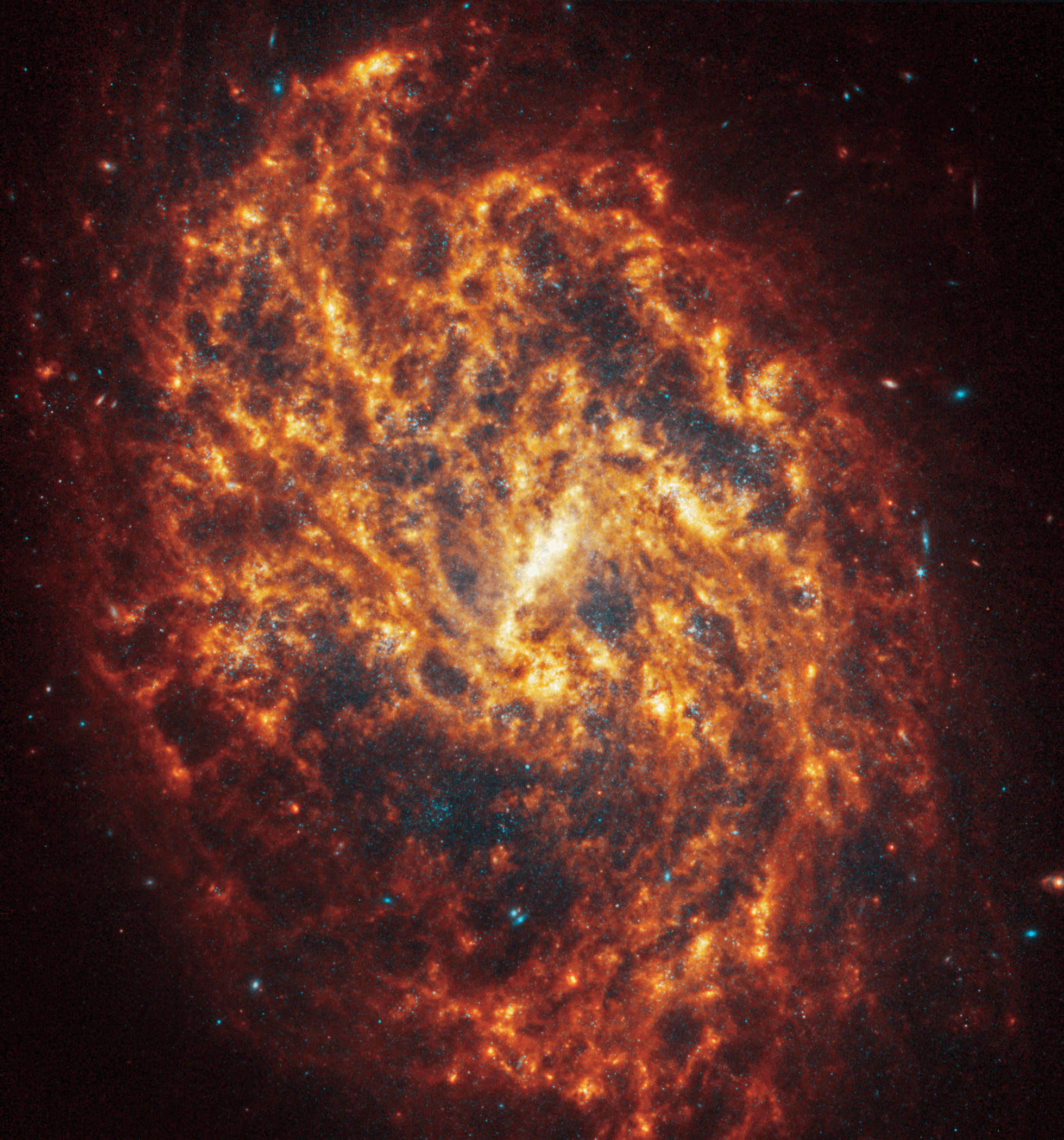

Spiral galaxy NGC 1087 is 80 million light-years away in the constellation Cetus.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Janice Lee (STScI), Thomas Williams (Oxford), and the PHANGS team
Follow the Spiral Arms
Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) captured millions of stars in these images, which sparkle in blue tones. Some stars are spread throughout the spiral arms, but others are clumped tightly together in star clusters.
The telescope’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) data highlights glowing dust, showing us where it exists around and between stars. It also spotlights stars that haven’t yet fully formed – they are still encased in the gas and dust that feed their growth, like bright red seeds at the tips of dusty peaks. “These are where we can find the newest, most massive stars in the galaxies,” said Erik Rosolowsky, a professor of physics at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Canada.
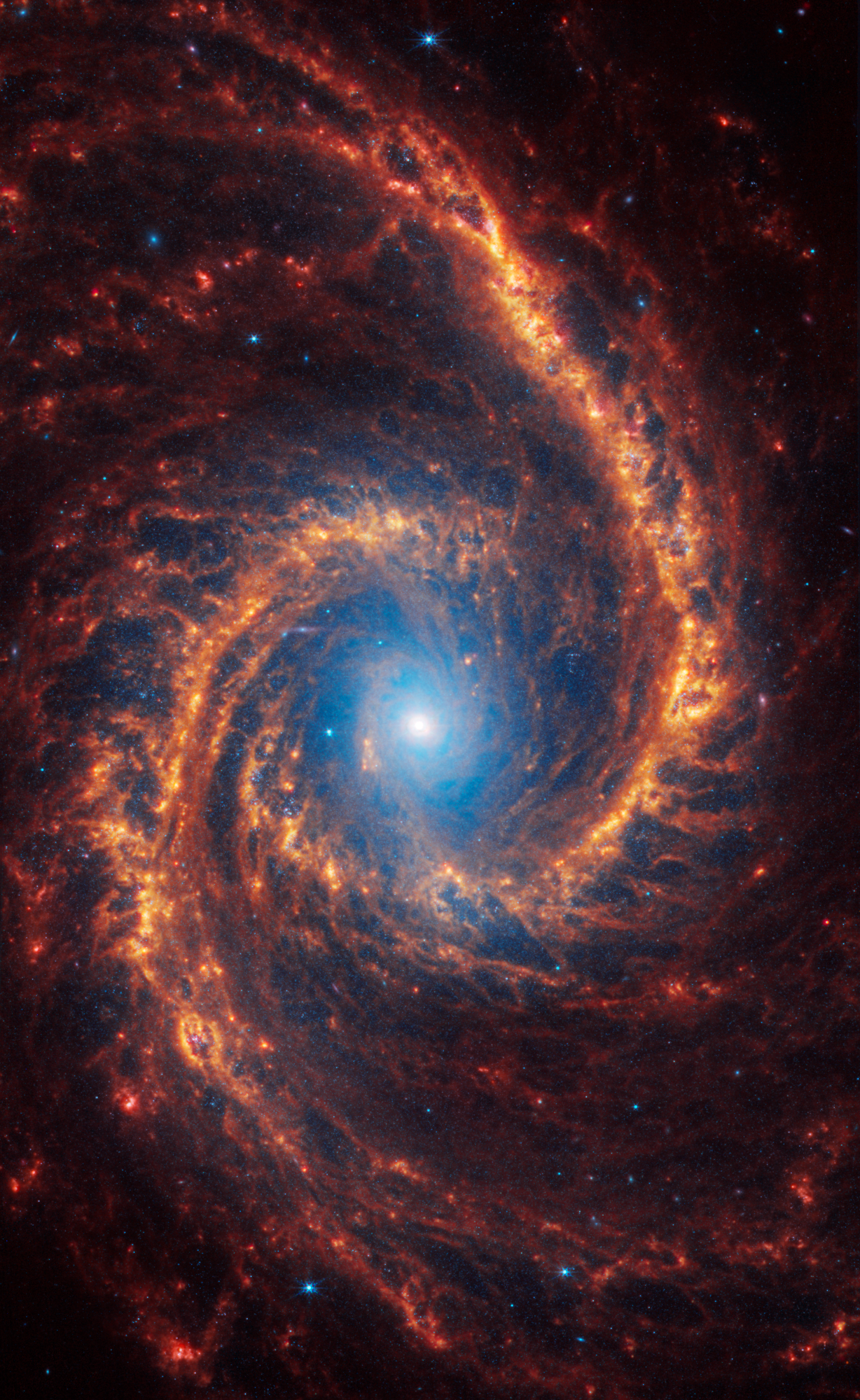

Spiral galaxy NGC 1566 is 60 million light-years away in the constellation Dorado.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Janice Lee (STScI), Thomas Williams (Oxford), and the PHANGS team
Something else that amazed astronomers? Webb’s images show large, spherical shells in the gas and dust. “These holes may have been created by one or more stars that exploded, carving out giant holes in the interstellar material,” explained Adam Leroy, a professor of astronomy at the Ohio State University in Columbus.
Now, trace the spiral arms to find extended regions of gas that appear red and orange. “These structures tend to follow the same pattern in certain parts of the galaxies,” Rosolowsky added. “We think of these like waves, and their spacing tells us a lot about how a galaxy distributes its gas and dust.” Study of these structures will provide key insights about how galaxies build, maintain, and shut off star formation.

Spiral galaxy NGC 2835 is 35 million light-years away in the constellation Hydra.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Janice Lee (STScI), Thomas Williams (Oxford), and the PHANGS team
Dive Into the Interior
Evidence shows that galaxies grow from inside out – star formation begins at galaxies’ cores and spreads along their arms, spiraling away from the center. The farther a star is from the galaxy’s core, the more likely it is to be younger. In contrast, the areas near the cores that look lit by a blue spotlight are populations of older stars.
What about galaxy cores that are awash in pink-and-red diffraction spikes? “That’s a clear sign that there may be an active supermassive black hole,” said Eva Schinnerer, a staff scientist at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Heidelberg, Germany. “Or, the star clusters toward the center are so bright that they have saturated that area of the image.”
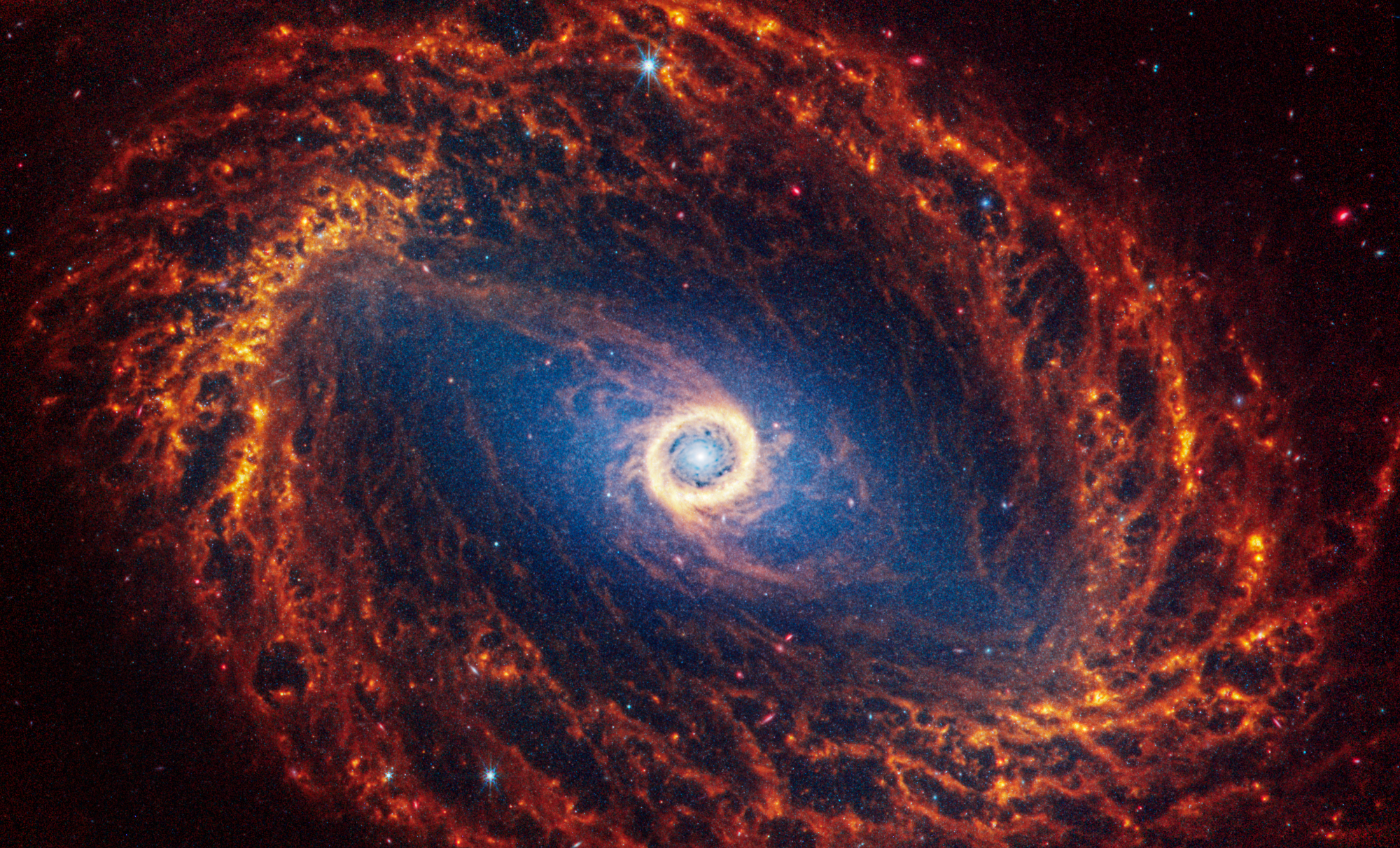

Spiral galaxy NGC 1512 is 30 million light-years away in the constellation Horologium.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Janice Lee (STScI), Thomas Williams (Oxford), and the PHANGS team
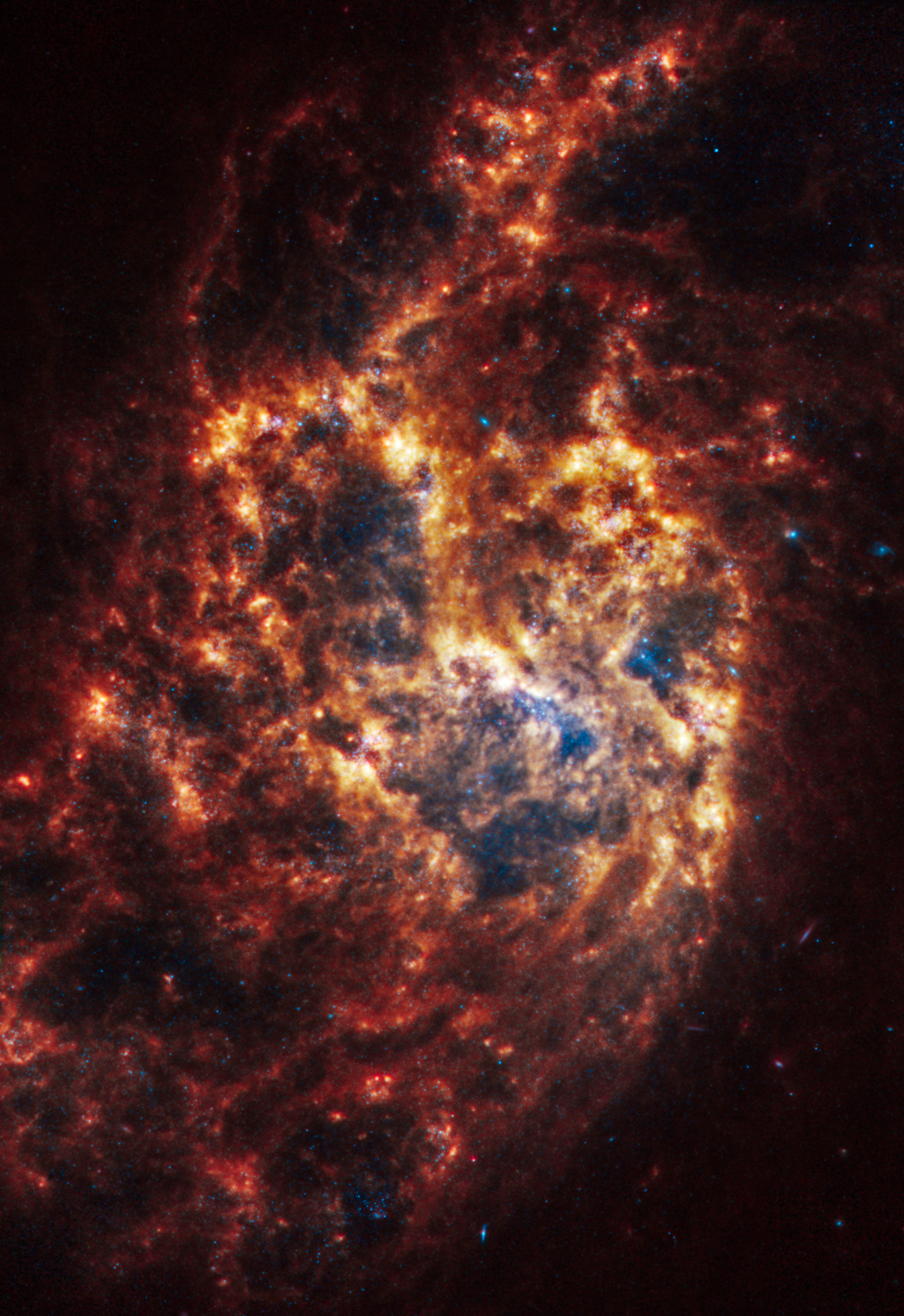

Spiral galaxy NGC 1385 is 30 million light-years away in the constellation Fornax.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Janice Lee (STScI), Thomas Williams (Oxford), and the PHANGS team
Research Galore
There are many avenues of research that scientists can begin to pursue with the combined PHANGS data, but the unprecedented number of stars Webb resolved are a great place to begin. “Stars can live for billions or trillions of years,” Leroy said. “By precisely cataloging all types of stars, we can build a more reliable, holistic view of their life cycles.”
In addition to immediately releasing these images, the PHANGS team has also released the largest catalog to date of roughly 100,000 star clusters. “The amount of analysis that can be done with these images is vastly larger than anything our team could possibly handle,” Rosolowsky emphasized. “We’re excited to support the community so all researchers can contribute.”
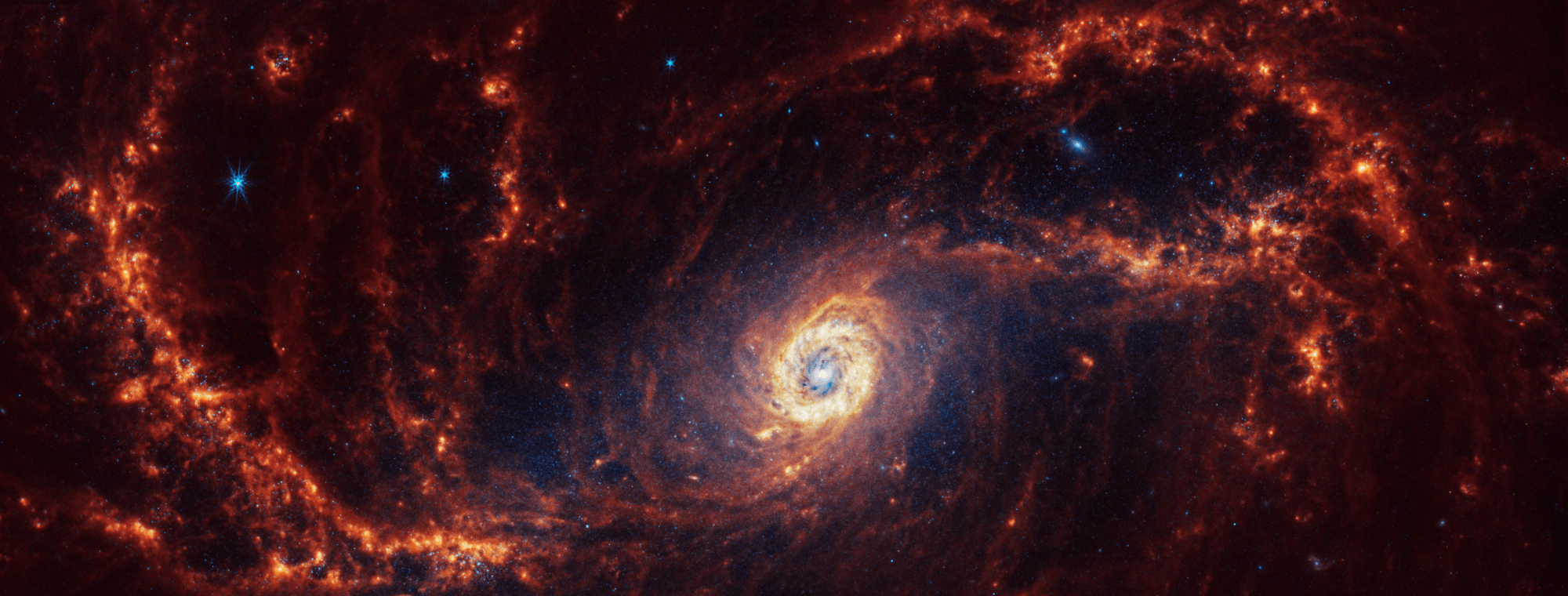
Spiral galaxy NGC 1672 is 60 million light-years away in the constellation Dorado.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Janice Lee (STScI), Thomas Williams (Oxford), and the PHANGS team
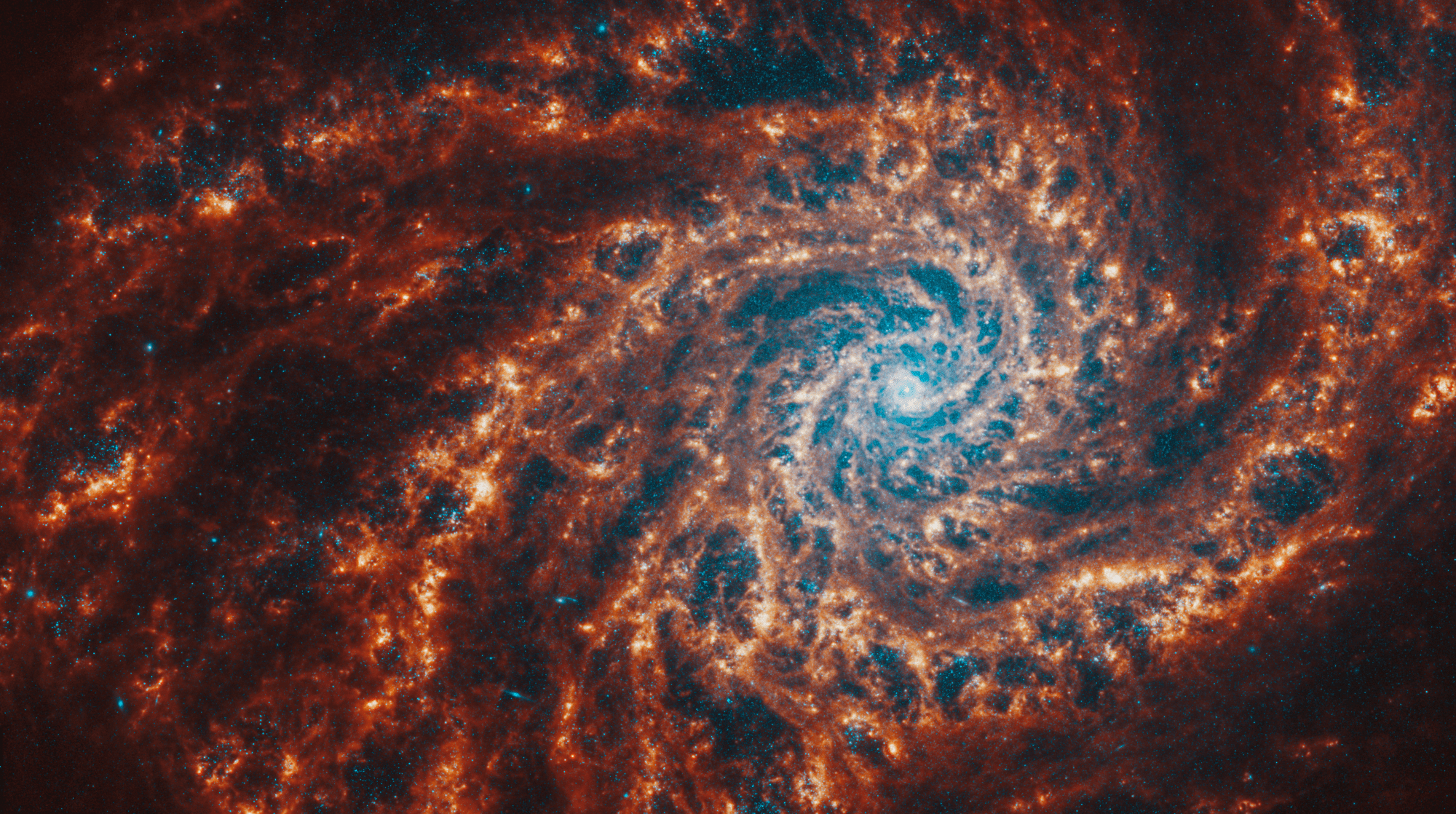
Webb Telescopes view face-on of spiral galaxy NGC 4254.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Janice Lee (STScI), Thomas Williams (Oxford), and the PHANGS team
See the full set of 19 images from both Webb and Hubble and download them at full resolution.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency.
Downloads
Right click the images in this article to open a larger version in a new tab/window.
Download full resolution images for this article from the Space Telescope Science Institute.
Access These Images on the MAST Archive
Media Contacts
Laura Betz/NASA – laura.e.betz@nasa.gov, Rob Gutro/NASA– rob.gutro@nasa.gov
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, , Greenbelt, Md.
Claire Blome – cblome@stsci.edu, Christine Pulliam/STScI – cpulliam@stsci.edu
Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, Md.
Related Information
Related Article: NASA’s Webb Reveals Intricate Networks of Gas and Dust in Nearby Galaxies
PHANGS Website for Researchers
Access These Images on the MAST Archive
More Webb News – https://science.nasa.gov/mission/webb/latestnews/
More Webb Images – https://science.nasa.gov/mission/webb/multimedia/images/
Webb Mission Page – https://science.nasa.gov/mission/webb/





