5 Surprising NASA Heliophysics Discoveries Not Related to the Sun
With NASA’s fleet of heliophysics spacecraft, scientists monitor our Sun and investigate its influences throughout the solar system. However, the fleet’s constant watch and often-unique perspectives sometimes create opportunities to make discoveries that no one expected, helping us to solve mysteries about of the solar system and beyond.
Here are five examples of breakthroughs made by NASA heliophysics missions in other fields of science.

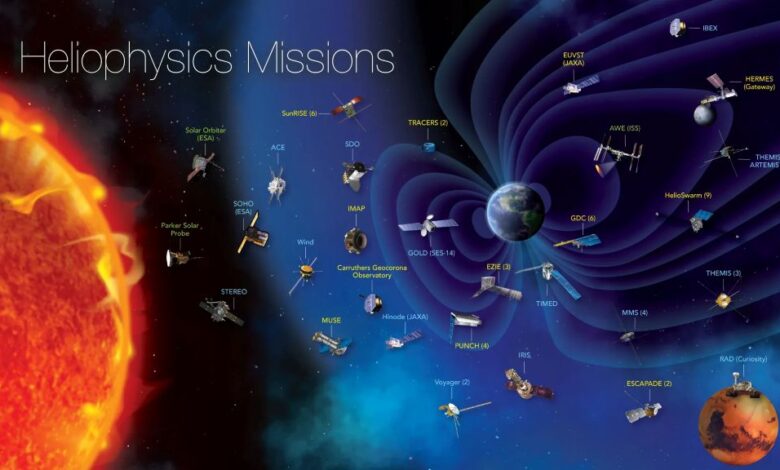
This graphic shows missions in NASA’s Heliophysics Division fleet as of July 2024.
NASA
Thousands and Thousands of Comets
The SOHO mission — short for Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, which is a joint mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA — has a coronagraph that blocks out the Sun in order to see the Sun’s faint outer atmosphere, or corona.
It turns out SOHO’s coronagraph also makes it easy to spot sungrazing comets, those that pass so close to the Sun that other observatories can’t see them against the brightness of our star.
Before SOHO was launched in December 1995, fewer than 20 sungrazing comets were known. Since then, SOHO has discovered more than 5,000.
The vast number of comets discovered using SOHO has allowed scientists to learn more about sungrazing comets and identify comet families, descended from ancestor comets that broke up long ago.

Two sungrazing comets fly close to the Sun in these images captured by ESA/NASA’s SOHO (Solar and Heliospheric Observatory). They were the 3,999th and 4,000th comets discovered in SOHO images.
ESA/NASA/SOHO/Karl Battams
Dimming of a Supergiant
In late 2019, the supergiant star Betelgeuse began dimming unexpectedly. Telescopes all over the world — and around it — tracked these changes until a few months later when Betelgeuse appeared too close to the Sun to observe. That’s when NASA’s STEREO (Sun-watching Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) came to the rescue.
For several weeks in the middle of 2020, STEREO was the only observatory able to see Betelgeuse. At the time, the STEREO-A spacecraft was trailing behind Earth, at a vantage point where Betelgeuse was still far enough away from the Sun to be seen. This allowed astronomers to keep tabs on the star while it was out of view from Earth.
STEREO’s observations revealed another unexpected dimming between June and August of 2020, when ground-based telescopes couldn’t view the star.
Astronomers later concluded that these dimming episodes were caused by an ejection of mass from Betelgeuse — like a coronal mass ejection from our Sun but with about 400 times more mass — which obscured part of the star’s bright surface.

The background image shows the star Betelgeuse as seen by the Heliospheric Imager aboard NASA’s STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) spacecraft. The inset figure shows measurements of Betelgeuse’s brightness taken by different observatories from late 2018 to late 2020. STEREO’s observations, marked in red, revealed an unexpected dimming in mid-2020 when Betelgeuse appeared too close to the Sun for other observatories to view it.
NASA/STEREO/HI (background); Dupree et al. (inset)
The Glowing Surface of Venus
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe studies the Sun’s corona up close — by flying through it. To dive into the Sun’s outer atmosphere, the spacecraft has flown past Venus several times, using the planet’s gravity to fling itself closer and closer to the Sun.
On July 11, 2020, during Parker’s third Venus flyby, scientists used Parker’s wide-field imager, called WISPR, to try to measure the speed of the clouds that obscure Venus’ surface. Surprisingly, WISPR not only observed the clouds, it also saw through them to the surface below.
The images from that flyby and the next (in 2021) revealed a faint glow from Venus’ hot surface in near-infrared light and long wavelengths of red (visible) light that maps distinctive features like mountainous regions, plains, and plateaus.
Scientists aimed WISPR at Venus again on Nov. 6, 2024, during Parker’s seventh flyby, observing a different part of the planet than previous flybys. With these images, they’re hoping to learn more about Venus’ surface geology, mineralogy, and evolution.

As Parker Solar Probe flew by Venus on its fourth flyby, it captured these images, strung into a video, showing bright and dark features on the nightside surface of the planet.
NASA/APL/NRL
The Brightest Gamma-Ray Burst
You’ve heard of the GOAT. But have you heard of the BOAT?
It stands for the “brightest of all time”, a gamma-ray burst discovered on Oct. 9, 2022.
A gamma-ray burst is a brief but intense eruption of gamma rays in space, lasting from seconds to hours.
This one, named GRB 221009A, glowed brilliantly for about 10 minutes in the constellation Sagitta before slowly fading.
The burst was detected by dozens of spacecraft, including NASA’s Wind, which studies the perpetual flow of particles from the Sun, called the solar wind, just before it reaches Earth.
Wind and NASA’s Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope measured the brightness of GRB 221009A, showing that it was 70 times brighter than any other gamma-ray burst ever recorded by humans — solidifying its status as the BOAT.

Astronomers think GRB 221009A represents the birth of a new black hole formed within the heart of a collapsing star. In this artist’s concept, the black hole drives powerful jets of particles traveling near the speed of light. The jets emit X-rays and gamma rays as they stream into space.
NASA/Swift/Cruz deWilde
A Volcano Blasts Its Way to Space
NASA’s ICON (Ionospheric Connection Explorer) launched in 2019 to study how Earth’s weather interacts with weather from space. When the underwater Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha‘apai volcano erupted on Jan. 15, 2022, ICON helped show that the volcano produced more than ash and tsunami waves — its effects reached the edge of space.
In the hours after the eruption, ICON detected hurricane-speed winds in the ionosphere — Earth’s electrified upper atmospheric layer at the edge of space. ICON clocked the wind speeds at up to 450 miles per hour, making them the strongest winds the mission had ever measured below 120 miles altitude.
The ESA Swarm mission revealed that these extreme winds altered an electric current in the ionosphere called the equatorial electrojet. After the eruption, the equatorial electrojet surged to five times its normal peak power and dramatically flipped direction.
Scientists were surprised that a volcano could affect the electrojet so severely — something they’d only seen during a strong geomagnetic storm caused by an eruption from the Sun.

The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai eruption on Jan. 15, 2022, caused many effects, some illustrated here, that were felt around the world and even into space. Some of those effects, like extreme winds and unusual electric currents were picked up by NASA’s ICON (Ionospheric Connection Explorer) mission and ESA’s (the European Space Agency) Swarm. Illustration is not to scale.
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Mary Pat Hrybyk-Keith
By Vanessa Thomas
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.





