NICER Status Update

NASA’s NICER Continues Science Operations Post Repair
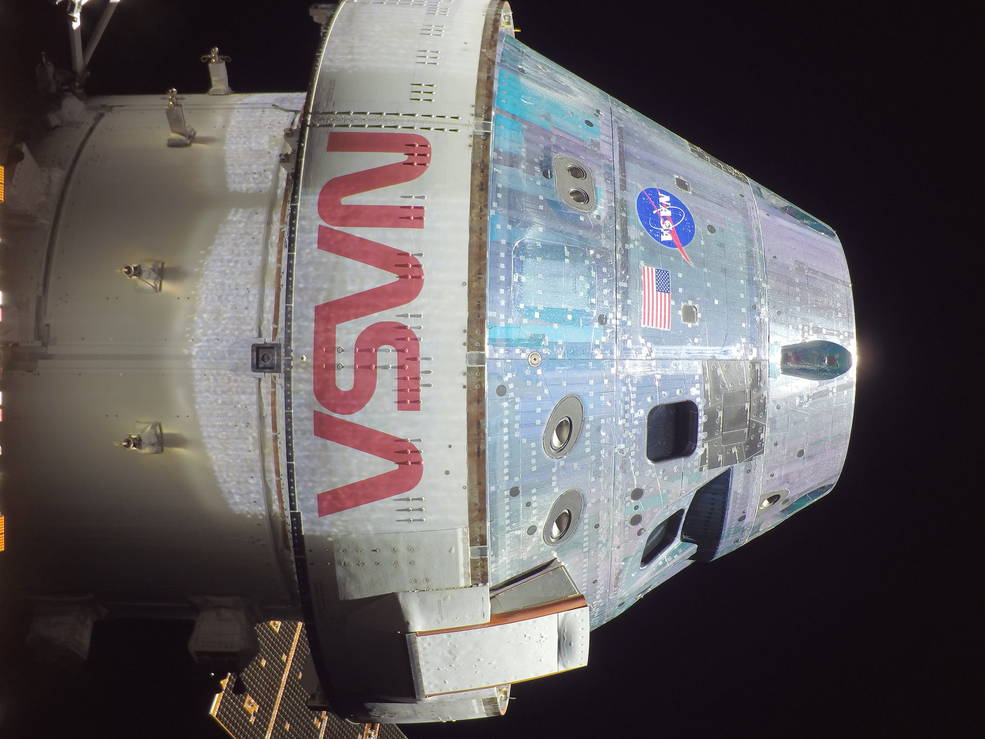
NASA crew aboard the International Space Station installed patches to the agency’s NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer) mission during a spacewalk on Jan. 16. NICER, an X-ray telescope perched near the station’s starboard solar array, resumed science operations later the same day.
The patches cover areas of NICER’s thermal shields where damage was discovered in May 2023. These thin filters block sunlight while allowing X-rays to pass through. After the discovery, the NICER team restricted their observations during the station’s daytime to avoid overwhelming the mission’s sensitive detectors. Nighttime observations were unaffected, and the team was able to continue collecting data for the science community to make groundbreaking measurements using the instrument’s full capabilities.
The repair went according to plan. Data since collected shows the detectors behind the patched areas are performing better than before during station night, and the overall level of sunlight inside NICER during the daytime is reduced substantially.
While NICER experiences less interference from sunlight than before, after analyzing initial data, the team has determined the telescope still experiences more interference than expected. The installed patches cover areas of known damage identified using astronomical observations and from photos taken by both external robotic cameras and astronauts inside the space station. Measurements collected since the repair and close-up, high-resolution photos obtained during the spacewalk are providing new information that may point the way toward further daytime data collection.
In the meantime, NICER continues operations with its full measurement capabilities during orbit night to enable further trailblazing discoveries in time domain and multimessenger astrophysics.
Media contact: Alise Fisher, NASA Headquarters / Claire Andreoli, NASA Goddard
June 8, 2023
Sunlight ‘Leak’ Impacting NASA’s NICER Telescope, Science Continues
On Tuesday, May 22, NASA’s NICER (Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer), an X-ray telescope on the International Space Station, developed a “light leak,” in which unwanted sunlight enters the instrument. While analyzing incoming data since then, the team identified an impact to daytime observations. Nighttime observations seem to be unaffected.
The team suspects that at least one of the thin thermal shields on NICER’s 56 X-ray Concentrators has been damaged, allowing sunlight to reach its sensitive detectors.
To mitigate the effects on measurements, the NICER team has limited daytime observations to objects far away from the Sun’s position in the sky. The team has also updated commands to NICER that automatically lower its sensitivity during the orbital day to reduce the effects from sunlight contamination. The team is evaluating these changes and assessing additional measures to reduce the impact on science observations.
To date, more than 300 scientific papers have used NICER observations, and the team is confident that NICER will continue to produce world-class science.